Adenoidectomy
Adenoid hypertrophy is a common finding in children, mainly below the age of 10 years.
The large adenoid pad in the post-nasal space may cause Obstructive Sleep Apnoea, post-nasal drip (yellow mucus) and cough, blocked nose, snoring and hearing loss (glue ear).
The symptoms are worse when the patient suffers from allergy / hay fever and asthma.
If these symptoms are present, the adenoid pad should be removed or better still, reduced.
The most common methods for adenoidectomy are:
• With a curette (removal of the adenoid commonly without use of a mirror, using a curette)
• With suction diathermy (monopolar electrocautery with the use of a mirror for anatomical orientation)
New dissection methods include Coblation (radio-frequency) adenoidectomy.
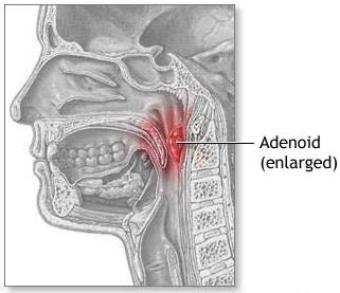
Diagram showing the location of the Adenoid
(Pharyngeal Tonsil)
Coblation Adenoidectomy
This is the method preferred by Anastasia Rachmanidou.
It is performed under general anaesthetic, through the mouth with the use of a mirror or a rigid endoscope and takes less than 10 minutes of surgical time.
The adenoid pad is reduced with very well-controlled dissection using the radio-frequency wand.
There is minimal bleeding during the adenoidectomy and none afterwards.
Children can go home 4 hours after surgery on antibiotics and pain-killers (up to 5 days).
Antibiotics are given on a prophylactic basis to reduce the risk of infection and prevent the bad smell that may develop from the back of the nose after an adenoidectomy.
Children can resume their normal activities after 5 – 7 days following the operation.
For more information and references please check
www.coblation.com
